American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, and Semimembranosus, which are posterior
thigh muscles, comprise the Hamstring muscle group.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: It flexes and rotates the leg, especially when the knee is flexed, and also extends the thigh.
Synergist: Antagonist: Iliopsoas, Pectineus, Tensor fasciae latae, Adductor brevis, Sartorius.
Nerve Supply: Sciatic Nerve.
Vascular supply: Supply: Profunda femoris artery.
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: The pain may be experienced while sleeping. The posterior leg pain is worsened during walking, and persistent sitting may result in deep buttocks, anterior thigh, or pain being experienced in the popliteal fossa. There is also pain when rising from a seated position.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Sitting in a chair where ones feet do not touch the floor for long periods of time.
Differential Diagnosis: (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) L5 radiculopathy, S1 or S2 Nerve Compression, Postlaminectomy pain syndrome, Bone cancer, Bone fracture, Pulled or torn Hamstring, Bruised ischial tuberosity, Deep vascular thrombosis (DVT), Lipedema, Multiple sclerosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Bursitis, Osteoarthritis, Tension Myalgia, Systemic lupus erythematosus, Fibromyalgia, Reflex sympathetic dystrophy (Complex regional pain syndrome), Coxa Plana, Cauda equina syndrome, Sprain/Strain, Systemic infections or inflammation, Eosinophilic fasciitis, Tetanus, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Biceps Femoris

Pointer Plus
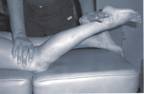
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()