American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
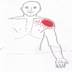
The Pectoralis major is a muscle of the chest.
Collectively with the Pectoralis Minor, they maybe referred to as the Pecs.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Adducts the arm, pulls it forward and rotates it internally.
Synergist: Pectoralis minor, Subclavius, Serratus anterior, Trapezius, Latissimus dorsi, Rhomboid major and minor, Levator scapulae.
Antagonist: Deltoid, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres major and minor, Subscapularis.
Nerve Supply: Medial and lateral Pectoral nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1).
Vascular supply: Pectoral branch of the thoracoacromial and the perforating branches of the interior thoracic artery.
Vascular entrapment: While there are no studies depicting neurovascular entrapment by the pectoralis major, Travell and Simonís state that entrapment of the axillary lymph nodes will result in breast swelling and tenderness.
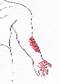
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Chest pain; front of shoulder pain; restricted shoulder abduction; subclavicular, arm, breast pain and tenderness.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Round shoulder posture, prolonged sitting while riding, slouched posture, heavy lifting, anxiety, sudden cooling of muscle.
Differential Diagnosis: Angina pectoris, Bicipital tendonitis, Costochondritis, Supraspinatus tendonitis, Subacromial Bursitis, Medial epicondylitis, Lateral epicondylitis, Pleurisy, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C5 C6 C7 C8 or T1 Radiculopathy, Intercostal neuritis, Lung cancer, Mastitis, Breast cancer, Menses, Fibrocystic Breast disease, Lymphatic cancer, Lymphedema, Lymphadenopathy, Myocardial infarction, Esophagitis, Gastroenteritis, Hiatal Hernia, Gallbladder Dysfunction, Polyneuropathy, Polymyalgia rheumatica, Fibromyalgia, Polymyositis, Systemic lupus erythematosus, Ankylosing spondylosis, Diabetic neuropathy, Osteoarthritis, Osteoporosis, Eosinophilic fasciitis, Tetanus, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Pectoralis Major

Pointer Plus

Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()