American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Latissimus Dorsi is a back muscle which connects the upper extremity to the spinal column.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Adducts, extends, and medially rotates the arm; pulls the shoulder downward and backward.
Synergist: Pectoralis major and minor, Subclavius, Serratus anterior, Trapezius, Rhomboid major and minor, Levator scapulae.
Antagonist: Deltoid, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres major and minor, Subscapularis.
Nerve Supply: Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8).
Vascular supply: Descending scapular, subscapular arteries.
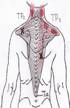
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Mid-back and arm pain.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Trauma, throwing a football, swinging a baseball bat, pull-ups, shoveling snow or dirt, constantly lifting heavy objects.
Differential Diagnosis: For shoulder blade and arm pain consider: C6 C7 or C8 radiculopathy, Angina pectoris, Myocardial infarction, Thoracic outlet syndrome, Brachial plexus entrapment, Entrapment of suprascapular nerve at the spine of the scapula, Pulmonary carcinoma, Adhesive capsulitis (Frozen shoulder), Ulnar Neuropathy, Bicipital tendinitis, Charcotís joint, Articular Dysfunction, Eosinophilic fasciitis, Tetanus, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication. For side pain consider: Slipped rib syndrome, Bruised ribs, Separated ribs, Rib fracture, Kidney infection, Possible Gallbladder pancreas hepatic (liver) or spleen involvement.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Latissimus Dorsi

Pointer Plus

Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral: