American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Supraspinatus is a rotator cuff muscle of the shoulder.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Assists in abduction of the arm, stabilizes the humerus in the glenoid cavity.
Synergist: Deltoid, Infraspinatus, Teres major and minor, Subscapularis.
Antagonist: Pectoralis major and minor, Subclavius, Serratus anterior, Trapezius, Latissimus dorsi, Rhomboid major and minor, and Levator scapulae.
Nerve Supply: Suprascapular Nerve (C4, C5, C6).
Vascular supply: Suprascapular artery.
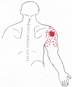
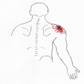
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: There is a dull aching pain during rest, which may be exacerbated with abduction. There is an expressed inability to abduct the arm as in combing ones hair or shaving ones face. Travell and Simonís state that frequently a popping sound may be heard when the shoulder is taken through ranges of motion.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Persistently working with outstretched arms, carrying heavy objects with ones arms at their side, sudden jerking motion of the arm when either at their side or when outreached.
Differential Diagnosis: (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C5 or C6 radiculopathy, Brachial plexus injuries, Thoracic outlet syndrome, Subdeltoid bursitis, Bicipital tendinitis, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Cervical arthritis or spurs, Rotator cuff tear, Rotator cuff tendinitis, Supraspinatus tendinitis, Neurogenic arthropathy (Charcotís joint), Adhesive capsulitis (Frozen shoulder), Brachial neuritis, Entrapment of the supraspinatus nerve, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy or Shoulder hand syndrome), Angina pectoris, Myocardial infarction, Pneumothorax, Bone cancer, Bone fracture, Dislocation/Subluxation of the Glenohumeral joint, Dislocation/Subluxation of the Acromioclavicular joint (Separated shoulder), Shoulder pointer, Sprain/Strain injury, Eosinophilic fasciitis, Tetanus, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Supraspinatus

Pointer Plus

Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()
![]()