American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Flexor Hallucis Longus is a deep posterior muscle of the leg.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Flexes the great toe and assist in the plantar flexing of the foot.
Synergist: Gastrocnemius, Flexor digitorum longus, Peroneus longus and brevis, Tibialis posterior, Soleus, Plantaris.
Antagonist: Extensor hallucis longus, Extensor digitorum longus, Tibialis anterior, Peroneus tertius.
Nerve Supply: Tibial Nerve (L5, S1, S2).
Nerve Entrapment: According to Travell and Simons, in concert with the Flexor Digitorum Longus, a Tarsal tunnel syndrome can develop.
Vascular supply: Peroneal artery.
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: The pain experienced in the great toe and the head of the 1st metatarsal joint is exacerbated during walking.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Persistent running or jogging on sloped or uneven surfaces, utilizing shoes that either do not cushion the balls of the feet or have inflexible soles, impaired mobility of the joints of the great toe.
Differential Diagnosis: Tarsal tunnel syndrome, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) L4 radiculopathy, Frostbite, Diabetic neuropathy, Polyneuropathy, Neurogenic arthropathy (Charcotís Joint), Gout, Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Bursitis, Turf toe, Paronychia (Ingrown toenail), Bunion/corns, Callus, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Flexor Hallucis Longus
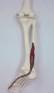
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()