American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
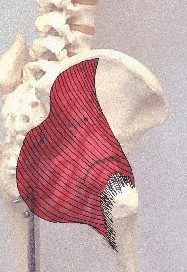
The Gluteus Maximus is a muscle of the gluteal region.
Collectively with the Gluteus Minimus and Gluteus Medius, they maybe referred
to as the Glutes.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Extends and laterally rotates the thigh.
Synergist: Antagonist: Iliopsoas, Pectineus, Tensor fasciae latae, Adductor brevis, Sartorius.
Nerve Supply: Inferior Gluteal Nerve (L5, S1, S2).
Nerve Entrapment: While no entrapment syndromes have been attributed to this muscle, Travell and Simons state that an entrapment syndrome is possible of the middle Cluneal nerve due to itís passing through the gluteus maximus to supply the skin.
Vascular supply: Superior and inferior gluteal artery.
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Cramping pain, restlessness and pain upon prolonged sitting.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: From a fall or a near fall, leaning forward while walking on uneven ground, swimming, over stretching the muscle, leg exercises, sitting too long in one position, a short first metatarsal bone, persistent sitting with a wallet in the hip pocket, direct trauma to the buttock region.
Differential Diagnosis: Trochanteric bursitis, Sacroiliac joint dysfunction, Lumbar articulating dysfunction, Inflammation of the sub gluteus medius bursa, S1 S2 S3 or S4 nerve compression, Articular dysfunction, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) Lower lumbar arthrosis herniation nerve compression (L4, L5 radiculopathy), Sciatica, Intervertebral stenosis, Hip Dislocation, Hip fracture, Hip Pointer, Tensor fasciae latae syndrome, Bone cancer or Malignant neoplasm of the hip, Sacroiliac joint displacement, Coccygodynia, Intervertebral stenosis, Reiterís disease, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Coxa plana,
Pregnancy, Osteoarthritis, Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (Complex regional pain syndrome), Polymyalgia rheumatica, Rheumatoid arthritis, Cauda equina syndrome, Eosinophilic fasciitis, Tetanus, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Gluteus Maximus

Pointer Plus
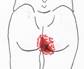
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()