American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Lumbricals are deep intrinsic muscles of the foot.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Flex the toes at the MP joints and extends the toes at the DIP and PIP joints.
Synergist: Quadratus plantae, Flexors Digitorum longus and brevis, Interossei.
Antagonist: Extensors Digitorum longus and brevis.
Nerve Supply: Medial plantar nerve (L4, L5), deep lateral plantar nerve (S1, S2).
Vascular supply: Plantar metatarsal artery.
Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: There is a difficulty in walking, paresthesia or edema of the foot, and deformity of the toes.
Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Wearing shoes that are too small, wearing a cast shoe for a long period of time, injury to the foot or toes.
Differential Diagnosis: Plantar fasciitis, Plantar warts, Hallux valgus, Stress fractures, Charcotís arthropathy, Frostbite, Diabetic neuropathy, Polyneuropathy, Foot trauma, Prolonged immobilization or dependency of the legs, Hammer toe, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) L4 L5 S1 or S2 radiculopathy, Nerve entrapment, If bilateral swelling consider Congestive heart disease (edema), Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Gout, injured sesamoid bone, Hip or knee discomfort secondary to antalgic gait, Osteoporosis, Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic dystrophy), Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication, With a positive Babinskiís toe sign suspect a Central nervous system (CNS) lesion.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Lumbricals

Pointer Plus
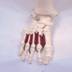
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral: