American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Splenius capitis is a posterior muscle of the neck.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Collectively, with the Splenius cervicis, extends the head and neck; and laterally flexes and rotates the head to the ipsilateral side.
Synergist: Semispinalis capitis and cervicis, Splenius cervicis, Spinalis cervicis, Interspinales, Longissimus cervicis, Iliocostalis cervicis, Multifidus. Antagonist: Sternocleidomastoid; Longus colli and capitis; Scalenus anterior, medius, and posterior.
Nerve Supply: Lateral branches of the dorsal primary division of the middle and lower cervical nerve. Vascular supply: The muscular branches of the occipital and superficial branch of the transverse cervical arteries.
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Headaches, neck pain, blurring of vision, pain on the crown of the head. Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Postural stresses e.g. bird-watching, sleeping without proper head support; acceleration/deceleration injury, sudden cooling of muscles, prolonged forward head bending. Differential Diagnosis: (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C1 radiculopathy (Bulging Prolapsed, Herniated Disc), C2 dysfunction, Occipitoatlantal dysfunction, Acceleration/Deceleration injury (Whiplash), Military neck (Absence of normal cervical spine lordosis), Cervical Spine Hyperlordosis, Vertebral vascular disorder, Cerebral aneurysm, Cerebral neoplasm (Brain cancer), Subacute meningitis, Encephalitis, Migraine headaches, Post concussion syndrome, Fibromyalgia, Polymyositis, Systemic lupus erythematosus, Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, Eye strain, Ocular disease, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Splenius Capitis

Pointer Plus
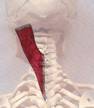
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()