American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
The Digastric is an anterior muscle of the neck.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Elevates and stabilizes the hyoid bone and raises the base of the tongue.
Synergist: Lateral Pterygoid, Stylohyoid, Suprahyoid, and Infrahyoid Antagonist: Masseter, Temporalis, Medial Pterygoid, and Superior division of lateral Pterygoid.
Nerve Supply: The Posterior belly – Facial Nerve (Cranial VII); the Anterior belly – Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial V). Vascular supply: The Posterior belly - Occipital and posterior auricular arteries; the Anterior belly
- Branches of the submental artery.
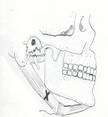
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: In addition to referral patterns,
there maybe difficulty in swallowing with exquisite tenderness experienced with palpation. While ipsilateral
visual blurring is usually associated with the SCM, this may occur occasionally with digastric involvement. Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Clinching the teeth, breathing from the
mouth, nasal disorders,
Trigger Points from the surrounding muscles, and acceleration/deceleration injuries. Differential Diagnosis: Eagle syndrome, Periapical infection, Polymyalgia rheumatica, Fibromyalgia, Carotid artery obstruction, Coronary involvement, Spasmodic torticollis (Wryneck syndrome), (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C2 radiculopathy, Broken tooth syndrome, disease of the lower incisors, Lymphedema,
Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Digastric

Pointer Plus
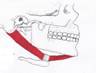
Travell and Simons Trigger Point Pain Referral:
![]()
![]()