American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
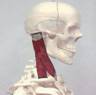
The Sternocleidomastoid is an anterior muscle of the neck.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Acting unilaterally – it draws the head toward the shoulder and rotates it pointing the chin superiorly and to the opposite side. Acting bilaterally – it flexes the head and raises the thorax when the head is fixed.
Synergist: Trapezius, Semispinalis capitis, Rectus capitis posterior major and minor, Oblique capitis superior, Splenius capitis, Longissimus capitis.
Antagonist: Longus capitis, Rectus capitis anticus.
Nerve Supply: Accessory Nerve (Cranial nerve XI). Nerve Entrapment: According to Travell and Simons, the Spinal accessory nerve (Cranial nerve XI) is occasionally entrapped in a hypertonic SCM, such as Wryneck or Spasmodic torticollis, with resulting paresis of the ipsilateral Trapezius.
Vascular supply: Sternocleidomastoid branch of the occipital and thyroid arteries, muscular of suprascapular artery, and the occipital of posterior auricular artery.
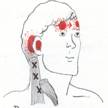
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Blurring of vision, unilateral deafness, soreness of neck, reddening of the conjunctiva, tearing of eyes, tension headaches, facial neuralgia, cervical cephalalgia, lymphadenopathy, stiff neck, dizziness, and vertigo. Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Recurrent infections, paradoxical breathing, sleeping on 2 pillows, structural inadequacies of the body, bird watching with binoculars, persistent cradling of a telephone receiver on one’s shoulder, tilting of head to one side, overhead work, painting, sheet rocking ceilings, vigorous rotation of the neck and head e.g. whiplash or trauma that may be experienced subsequent to sporting endeavors. Differential Diagnosis: Ménière’s disease, Cerebellopontine tumors, Intracranial vascular lesions, Multiple sclerosis, Inflammation of labyrinth, Hemorrhage into pons, Epilepsy (Seizure disorder), Neurological disease, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C1 or C2 radiculopathy, Subacute meningitis or Peripheral neuropathy, Polyneuropathy, Polymyalgia rheumatica, Fibromyalgia, Carotid or vertebral artery obstruction, Cerebral aneurysm, Vestibular disease, Tetanus, Congenital and Spasmodic torticollis (Wryneck syndrome), Trigeminal neuralgia (Tic douloureux), Headaches, Tension myalgia, Somatization disorder, Ocular Disease, Stinger or burner, Acceleration/Deceleration injury (Whiplash), Hangover, Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)

Pointer Plus
![]()