American
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine
|
American
|
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
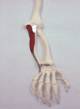
The Flexor carpi ulnaris is a superficial anterior muscle of the forearm.
Anatomical Attachments: Action: Flexes and adducts the wrist and the hand, and aids with flexion of the forearm.
Synergist: Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus. Antagonist: Abductor pollicis longus, Flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus, Flexor pollicis longus.
Nerve Supply: Ulnar Nerve (C8, T1). Nerve Entrapment: Entraps the ulnar nerve.
Vascular supply: Posterior ulnar recurrent artery.
Click on a small image to view an enlarged image Trigger Point Signs and Symptoms: Pain during activities requiring gripping and wrist flexion. Trigger Point Activating and Perpetuating Factors: Persistent or sustained gripping with wrist flexion, which is
frequently observed in persons who cup their hands over the end of a chair; skiers as a result of gripping poles or handles;
construction workers who use hand tools, which are either heavy or have persistent vibration such as jackhammers, saws or
drills Differential Diagnosis: Medial epicondylitis, Ulnar neuropathy, Carpal tunnel syndrome, Charcotís arthropathy,
Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis of wrist, (Segmental, Subluxation, Somatic dysfunction) C5 radiculopathy, Subacute
meningitis or Peripheral neuropathy, Dupuytrenís contracture, Diabetic neuropathy, Polyneuropathy, Systemic lupus
erythematosus, Complex regional pain syndrome (Reflex sympathetic Dystrophy),
Systemic infections or inflammation, Nutritional inadequacy, Metabolic imbalance, Toxicity, Side effects of medication.
Home
Search
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
About us
Contact us
Site map
Continuing Education © Copyright
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris

Pointer Plus
![]()