Home
Pain referral
Trigger points
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
Historical
Cranial nerve V - the Trigeminal nerve
Signs and Symptoms of Lesions
The individual may experience loss of
sensation or shooting facial pain; paresthesia; paralysis of mastication
muscles; loss of reflexes; impaired hearing; lockjaw; dryness of nose or
ulceration’s of the face.
Trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux) is
typified by a sharp lancinating pain of at least one of the branches of the
trigeminal nerve. While it lasts only a short while, the pain is excruciating,
and usually unilateral, and may be triggered by temperature change, a blast of
air, chewing or stress.
Trigeminal
Nerve Test
There are three steps in which to test
Cranial Nerve V.
1.
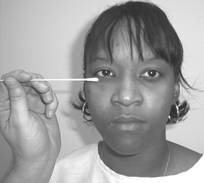
Test sensation – With the individuals’ eyes closed, the practitioner will use a cotton swab or pointy
object over the face and the anterior half of the scalp. Have the individual
tell you where they are feeling the object.
|
|

Trigeminal nerve test 1
|
|
2.
Reflex – With the individual's eyes open and looking
upward, the practitioner takes a strand of cotton, approaches the cornea from
the side, and touches it with the cotton. This should initiate a blink
response. Both eyes should be tested independently, with a failure to blink
being presumptive of a positive response.
|
|
Trigeminal nerve test 2
|
|
3.
Initially, the practitioner has the individual clinch his/her jaw and palpates
contractile response of the masseter slightly superior to the mandibular ramus.
Then the practitioner applies moderate pressure to the mandibular symphysis and
requests the individual to open against load. Lateral deviations of the
mandible should be noted for muscle weakness or uneven tensile compression, if
so consider temporal mandibular joint dysfunction or Myofascial Pain Dysfunction
Syndrome. Inability to perform successfully, infers possible paralysis as
observed in Bell’s palsy and Cerebral Vascular disorders.
|
|
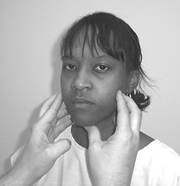
Trigeminal nerve test 3
|
|
When accompanied by pain, consider trigeminal neuralgia (tic douloureux), post
herpatic neuralgia (Ramsey Hunt syndrome or
herpes zoster oticus), temporomandibular joint
dysfunction or TrP referral from the SCM or the Masticatory muscles. With facial
ulcers consider active herpes zoster (Ramsey Hunt Syndrome or
herpes zoster oticus).
With impaired hearing, consider cerumen
buildup and nerve deafness; and perform the Acoustic Nerve test - Cranial
Nerve VIII.
Back to Top
About us
Contact us
© Copyright American Academy of Manual Medicine. 2001, 2007, 2008. All rights reserved.
![]() f
Manual
Medicine
f
Manual
Medicine


